Learn the Present Perfect Tense

Let's learn how to form the present perfect tense.
This tense is formed using the auxilliary verb "have" (have /has) plus the past participle of the main verb. We'll learn how to make positive and negative forms, short forms (contractions) and questions.
[Note: Click here to learn how to use the present perfect.]
Present Perfect Affirmative Statements
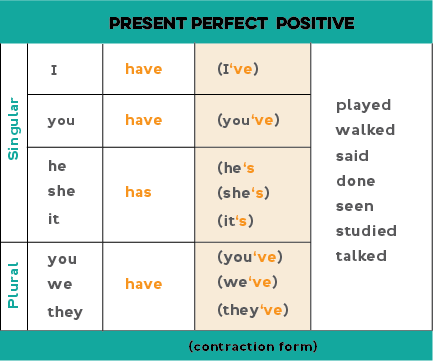
To form the present perfect: we use "have" / "has" + the past participle.
Note: You can also use contractions: I have = I've; you have = you've; he has = he's; she has = she's we have = we've; they have = they've
To form the past participle: add "ed" to the infinitive form of regular verbs. We use the same form for each subject (e.g., I, you, he).
- I have started the car. (start — started)
- I've started my book report.
- She has worked as a cashier before. (work — worked)
- She's worked here for 20 years.
- It has rained for three days now. (rain — rained)
- It's rained all day.
- The store has opened. (open — opened)
- We've already talked about this. (talk — talked)
- You've watched that movie many times before. (watched — watched)
Spelling Changes with Past Participles
Sometimes there are spelling changes when forming the past participle:
1. If the verb ends with "y", we change it to -i and add -ed (but only if there's a consonant before the -y):
- Have you tried the cupcakes? They're delicious! (try — tried)
- We've studied the present perfect but not the past perfect. (study — studied)
- I've cried about this for months. (cry — cried)
- My assistant has copied the report for the meeting. (copy — copied)
2. If the verb ends with "e" , we add just a "d" (not "ed"):
- Has the bank already closed? (close — closed, NOT: closeed)
- She has measured the ingredients for the recipe. (measure — measured)
3. Double the final consonant after a short stressed vowel if the verb ends in a CVC (consonant vowel consonant)*:
- I have stopped drinking alcohol for now. (stop — stopped: double the "p" then add "ed")
- She has planned a surprise for dinner. (plan — planned)
(*except CVC endings with w, x, or y)
Irregular Past Participle Forms
Many verbs have irregular past participles.
Examples:
- We have eaten all the cake. (NOT: we have "eated")
- I have done my homework already. (NOT: "doded")
- Help! My dog has run away. (NOT: "runned")
Unfortunately, you have to memorize them. Here are many of the irregular forms:
|
be — been become — become begin — begun break — broken bring — brought buy — bought catch — caught choose — chosen come — come cost — cost cut — cut do — done draw — drawn drink — drunk drive — driven eat — eaten fall — fallen feel — felt fight — fought |
find — found fly — flown forget — forgotten get — gotten give — given go — gone grow — grown hang — hung have — had hear — heard hide — hidden hit — hit hold — held hurt — hurt keep — kept know — known leave — left lend — lent let — let |
light — lit lose — lost make — made mean — meant meet — met pay — paid put — put read — read ride — ridden ring — rung rise — risen run — run say — said see — seen sell — sold send — sent shine — shone shoot — shot shut — shut |
sing — sung sit — sat sleep — slept speak — spoken spend — spent stand — stood steal — stolen swim — swum take — taken teach — taught tear — torn tell — told think — thought throw — thrown wake — woken wear — worn win — won write — written |
Present Perfect Negative Statements
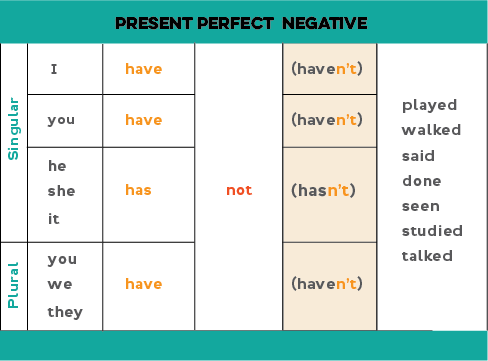
To form the negative, simply add "not" after "have" / "has":
- subject + has / have + not + past participle
We can also use the contractions hasn't / haven't (has not = hasn't, have not = haven't)
Examples:
- They haven't come to my house before.
- They have not found the restaurant yet.
- I have not started cleaning yet.
- I haven't heard any noises from our neighbors today.
- Don't worry my dog hasn't ever bitten anyone.
- My cat has not killed any mice.
Yes / No Questions

To form questions use:
- Have / has + subject + past participle
Examples:
- Have you seen this movie before?
- Has the number 10 bus come yet?
- Have they gone to bed already?
- Has Marie lost weight?
- Have you missed me since I left?
We can answer no questions with a full or a shorter answer by using contractions (hasn't / haven't) with negative answers.
Examples:
Have you done your homework?
- Yes, I have done my homework.
- Yes, I have. (short answer)
- No, I have not done my homework.
- No, I haven't. (short answer)
Have they eaten?
- Yes, they have eaten.
- Yes, they have. (short answer)
- No, they have not eaten.
- No, they haven't. (short answer)
Wh- Questions Present Perfect
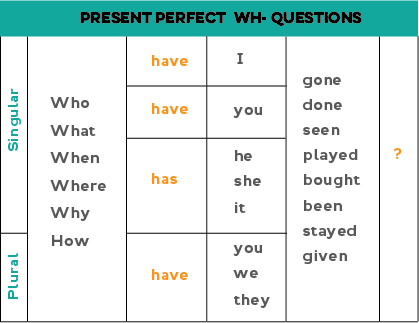
Notice the word order. The wh- question word comes before "have / has " and then the past participle.
Examples:
- How long have you studied English?
- Where has your mother gone?
- Why has the train stopped here?
- Who have they hired to organize the conference?
- What has the girl brought in her bag?
- How much of the meat has your dog eaten?
Whew! We covered a lot of information on this page. Check back for exercises that will help you practice the present perfect in its different forms.
Click here to learn when to USE the present perfect.
- Home Page ›
- Main Grammar Page ›
- Present Perfect
